What is Pepsin, and What Does Pepsin Do?
The role of pepsin in the digestive system should not be underestimated. Learn why pepsin is the silent champion in the pursuit of athletic excellence.More
The importance of nutrition in athletic performance and well-being cannot be overstated. Among the numerous components that contribute to a balanced and effective diet, the role of enzymes, specifically pepsin, takes center stage. Pepsin, a digestive enzyme produced in the stomach, plays a crucial role in breaking down dietary proteins into essential amino acids.
Understanding the importance of pepsin is essential to optimizing nutrient absorption, supporting muscle repair, and enhancing overall health for athletes whose bodies undergo rigorous training and recovery processes.
In this article, we look at the key benefits of pepsin and how it affects the health and performance of athletes.
What is Pepsin?

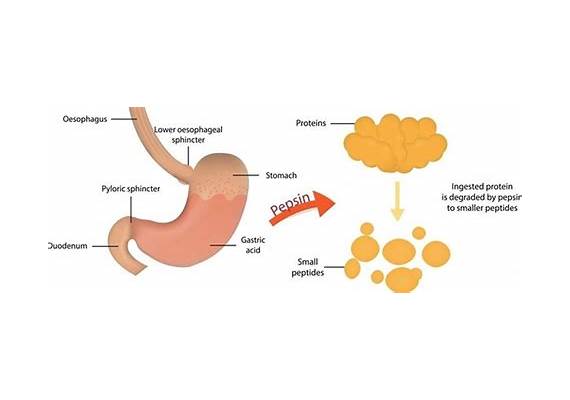
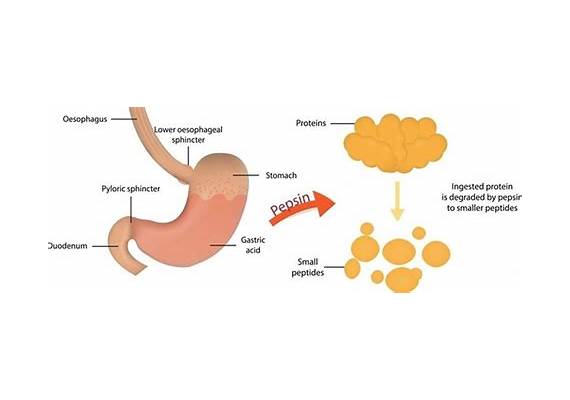
Pepsin is an enzyme that is produced and released by cells in the gastric glands of the stomach, and it plays a crucial role in the digestion of proteins in the stomach. The primary function of pepsin is to break down large protein molecules into smaller peptides.
Initially, the gastric chief cells (also known as zymogenic cells or peptic cells) in the stomach lining produce pepsin in an inactive form known as pepsinogen.
The gastric parietal cells in the stomach lining secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) to convert pepsinogen into its active form, pepsin.
Once activated, pepsin activates the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins, breaking them down into smaller peptides. Once the partially digested food, now called chyme, moves into the small intestine, the pH becomes less acidic, and other digestive enzymes take over the process of breaking down proteins further.
What Does Pepsin Do?

The primary function of pepsin is the role of breaking down protein in the digestive process.
— Nutrient Absorption: Pepsin helps break down proteins into smaller peptides. This helps absorb amino acids, which are not only important for protein synthesis, but also serve as precursors for various essential molecules in the body. Amino acids play roles in the synthesis of enzymes, hormones, neurotransmitters, and other vital substances.
— Immune Function: Proteins are essential for a strong immune system. By breaking down proteins, pepsin contributes to the availability of amino acids necessary for the synthesis of immune-related molecules. Proper protein digestion supports overall immune function and helps the body defend against infections and diseases.
— Overall Digestive Health: Pepsin, along with other digestive enzymes and gastric juices, contributes to the maintenance of a healthy digestive system. The lack of pepsin could lead to undigested proteins reaching the small intestine in large, intact forms, which could potentially cause digestive discomfort or other issues.
Therefore, it's essential to note that while pepsin has these benefits, an imbalance in the digestive system or certain medical conditions can sometimes lead to issues such as gastric ulcers or reflux. In such cases, the acidic contents of the stomach, including pepsin, may cause irritation to the esophagus or other parts of the digestive tract. Individuals with digestive concerns should consult healthcare professionals for appropriate guidance and management.
How Does Pepsin Benefit Athletes?

Pepsin, and the role it plays in the digestion of dietary proteins, is important in the overall health of athletes and fitness enthusiasts and their ability to perform at their best. Proteins are essential macronutrients for athletes as they provide the building blocks (amino acids) necessary for muscle repair, growth, and overall recovery. Here's how pepsin and protein digestion are relevant to athletes:
- Muscle Repair and Growth: Physical activity, especially intense exercise, leads to muscle damage. Repairing and rebuilding these damaged muscles require adequate protein intake, which is crucial for contributing to overall muscle growth and strength. Pepsin's role in breaking down dietary proteins into smaller peptides facilitates the absorption of amino acids, which are then used for muscle protein synthesis.
- Recovery: Rigorous training sessions can deplete glycogen stores and cause muscle fatigue. Protein consumption post-exercise, along with carbohydrate intake, helps replenish glycogen stores and promotes muscle recovery. Pepsin contributes to the breakdown of protein into amino acids, facilitating the rapid availability of these building blocks for the recovery process.
- Protein Utilization: Athletes need more protein than sedentary individuals, due to the higher demands on muscle protein turnover. Efficient protein digestion, facilitated by pepsin, ensures that the body can effectively utilize the ingested protein for various physiological functions, including energy production, immune function, and enzyme synthesis.
- Nutrient Absorption: Beyond proteins, pepsin also aids in the digestion of other nutrients. A healthy digestive system is essential for the absorption of various micronutrients necessary for overall health and performance. Proper nutrient absorption supports energy metabolism, immune function, and overall well-being.
While pepsin is vital for breaking down protein for digestion, it's important to note that overall digestive health is key for athletes. They should pay attention to their diet, ensuring an adequate intake of not only proteins but also carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
Furthermore, hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal digestive function. Athletes often work with nutritionists and dietitians to tailor their diets to meet their specific energy and nutrient requirements.
Bottom Line
In the dynamic world of sports, where the pursuit of peak performance is relentless, the role of pepsin in the digestive orchestra cannot be underestimated. Its ability to break down proteins into the foundational blocks of amino acids holds the key to efficient muscle repair, robust immune function, and sustained energy levels.
As athletes meticulously craft their nutrition plans, the awareness of pepsin's importance becomes a valuable asset. There is a synergy between pepsin and athletic endeavors that underscores the interconnectedness of digestive wellness and optimal performance. As we navigate the intricacies of sports nutrition, let us not overlook the silent champion, pepsin, in the pursuit of athletic excellence and enduring health.
Pepsin /ˈpɛpsɪn/ is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site.
PEPSIN FUNCTION


 mainadmin
mainadmin 










